What was the Inquisition? – 1
The Inquisition has long been made to look monstrous. The Essential Catholic Survival Guide reckons that “to non-Catholics it is a scandal; to Catholics, an embarrassment; to both, a confusion.” Indeed, our generation shies away from its memory or, if caught on the back foot, quickly turns apologetic. It is as though we are under a spell, and this is the handiwork of those inimical to the Catholic Church or at least unaware of the real functioning of the court that was the Inquisition.
The point here is not to whitewash a much maligned institution but to understand its nature. We are before a formal tribunal, not a mere people’s court; that this court had well established procedures, similar to modern courts in many ways and, obviously, following contemporaneous standards of justice, however alien they may seem to our generation. And given the lack of documentation, it is unreasonable to depend on statistics alone to make up our minds about that institution.
Definitions

‘Inquisition’ and ‘Heresy’ are two terms that call for special attention. The first one, from the Latin inquirere, meaning “to inquire”, refers to questioning. Roman law provided for an inquisitorial procedure by magistrates investigating crimes in the absence of formal charges being brought to their attention. After the Empire converted to Christianity in the fourth century, the procedure was employed by emperors from Constantine onwards to investigate heresy and related cases. It behoved the State to uproot this crime which always had socio-political implications; it was only in the second millennium that the Pope intervened, to rein in excesses, by setting up a formal tribunal, though not fully successfully.
Heresy isn’t the same thing as incredulity, schism, apostasy or some such sin against the faith. The Catechism of the Catholic Church defines heresy as “the obstinate post-baptismal denial of some truth that must be believed with divine and Catholic faith; or it is likewise an obstinate doubt concerning the same.” The doubt or denial involved in heresy concerns a matter that has been revealed by God and solemnly defined by the Church, be it the Holy Trinity, the Incarnation, the Real Presence of Christ in the Eucharist, the Holy Sacrifice of the Mass, Papal Infallibility, the Immaculate Conception and Assumption of Mary.
It was the task of the Inquisition to ascertain whether a person was guilty of propagating a heresy. Mere holding of wrong notions of Catholic doctrine privately did not attract sanctions from the court. Only a person found to be spreading those views came under the scanner of the Inquisition; and only refusing to be corrected would be considered heretics.
The Inquisition judged Christians; it was thus no torture plan to convert people to Christianity, as it is made out to be. Neither was it an instrument of evangelisation nor were there ever any provisions under Church law for the use of force to convert a person to the faith. The Inquisition aimed primarily to try and reform the accused and win them back to the faith. However, as heresy was an offence under the law, the tribunal, like a parent punishing an intractable child, would have hardened offenders penalised, so as to safeguard the common good. In those days, when Church and State were united, like soul and body, the law holistically catered to the citizens’ spiritual and material welfare. It goes without saying that very often the State overruled the Church, disparaging the spiritual and reformatory aspect and exalting the material and punitive side.
Historical development

Like Moses who was anguished by his people’s worship of the Golden Calf, the Christian Apostles too were deeply concerned about guarding and transmitting the deposit of the Faith undefiled. Unfortunately, not only the early days of Christianity, the whole of the first millennium was riddled with heretical doctrines: the Circumcision heresy (1st c.); Gnosticism (1st-2nd cs.); Montanism (late 2nd c.); Sabellianism (early 3rd c.); Arianism (4th c.); Pelagianism and Semi-Pelagianism (5th c.); Nestorianism (5th c.); Monophysitism (5th c.); Iconoclasm (7th-8th cs.) and Catharism (11th c.). The Church authorities suffered the consequences of those heresies but, rather than opting for the Old Covenant penalties of death or scourging, simply excommunicated the heretic.
On the other hand, the imperial successors of Constantine, who regarded themselves as masters of the temporal and material conditions of the Church, were persuaded that it was their first concern to protect the State religion. Heresies generated anarchy, so penal edicts (confiscation of property and death) were issued regularly against heretics. A law of the year 407 asserts for the first time that heresies ought to be equated with high treason. For their part, the church authorities in the Christianised states of the Roman Empire refused to invoke the civil power against the heretics.
Ironically, it was the heretics who appealed to the civil power for protection against the Church, and before long complained bitterly of administrative cruelty. At this point, Bishop St Optatus of Mileve defended the civil authority, thus championing for the first time a decisive cooperation of the State in religious questions and its right to inflict death on heretics. This matter wasn’t settled unequivocally given that several ecclesiastical authorities declared that the death penalty was contrary to the spirit of the Gospel. St Augustine was one such bishop who tried to lead back the erring by means of instruction. However, he changed his views, perhaps moved by the incredible excesses perpetrated by the heretics. Yet, it was the desire of the bishop of Hippo to correct them, not put them to death; he wanted the triumph of ecclesiastical discipline, not the death penalties that they deserved.
Meanwhile, as often as the social welfare required it, Christian rulers sought to stem the evil with appropriate measures. In an attempt to save the kingdom and save souls, even distinguished citizens, ecclesiastical and lay, were burnt at the stake. Often there were outbursts of Christian popular sentiment against dangerous sectaries. Sometimes the people blamed the clerical softness in pursuing heretics and so took the law into their hands. Kings and bishops responded by condemning heretics to the stake to prevent the spread of what they called “the heretical leprosy”.

According to the Catholic Encyclopaedia, a definitive strategy came about after Frederick Barbarossa, the powerful king of Germany and Sicily, and Pope Alexander III reached an accord reconciling their respective powers in the Peace of Venice in 1177. This was reaffirmed at the Lateran Council of 1179. In 1184, Pope Lucius III issued the decretal Ad abolendam (‘To abolish diverse malignant heresies’) which some have called the “founding charter of the Inquisition”. It commanded bishops to take an active role in identifying and prosecuting heresy in their jurisdictions. Heretics would suffer excommunication from the Church and be handed over to the civil power to be punished according to the provisions of the common law.
Accordingly, the first Inquisition tribunal was established in southern France in 1184. While death was still not on the cards, punishment was limited to exile, expropriation, destruction of the culprits dwelling, infamy, debarment from public office, and the like. The explicit identification of heresy with treason and its prosecution according to the norms of Roman law was formalised in 1199 by Pope Innocent III. At the Lateran Council of 1215, a relative service was done to the heretics by the introduction of regular canonical procedure to abrogate the arbitrariness, passion and injustice of the civil courts and from the penal codes in Spain, France and Germany.
New Challenges

Although medieval Europe was a society of Catholic kingdoms, adherents of other religions, particularly Judaism and Islam, also lived there. In the first few decades of the thirteenth century, Christian Europe was so endangered by heresy that a formal ecclesiastical tribunal under direct papal jurisdiction became a social, religious and political necessity. Pope Gregory IX established the so-called Monastic Inquisition by his Bulls of 13, 20, and 22 April 1233, appointing Dominican monks as the official inquisitors for all dioceses of France. The Inquisition had jurisdiction only over the Catholic populace; non-Catholics would be hauled up only if found to be perverting Catholic mores. At a time when the people had higher regard for the soul than for the body, heresies were spiritual terrorism to be tackled with vehemence, just as we do against acts of physical violence today.
Broadly speaking, the new tribunals of the Inquisition established in Europe and Asia faced many challenges, some of which are listed below:
a) Catharism (13th century)
These sects were a social menace right from the Byzantine period. They were treated with severity, yet they poured over all of Western Europe. A mix of religions reworked with Christian terminology, Catharism was an umbrella for multiple sects, one of the largest being the Albigensians. By and large, they were not only hostile to the Mass, the sacraments, the ecclesiastical hierarchy and organization, and to the government; their views were fatal to the continuance of human society as they forbade marriage and made a duty of suicide. It was only natural that both Christian and non-Christian custodians of the existing order in Europe should adopt repressive measures against their aberrant teachings.
b) Conversos (15th century)
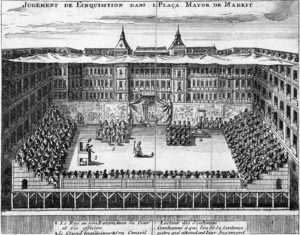
Pope Sixtus IV empowered Ferdinand and Isabella to set up the Inquisition in Spain in the year 1478, to confront the conversos, pseudo-converts from Judaism (Marranos) and from Islam (Mouriscos). The tribunal turned very fierce even by the standards of the time, so much so that the Pope made efforts to limit the powers of the inquisitors but to hardly any avail. In 1483, a Grand Inquisitor and Supreme Council was appointed to supervise local inquisitorial tribunals, including the later ones in Mexico and Peru. The first Grand Inquisitor, the Dominican Tomás de Torquemada, also exceeded his powers.
c) Protestantism (16th century)
At the turn of the sixteenth century, Europe found itself divided into two ideological blocs: one Catholic and obedient to the Pope; the other, Protestant and opposed to the Pope. After Luther, Calvin and Henry VIII parted ways with the Catholic Church, each began spreading theological ideas that were in conflict with the teachings of the Catholic Church. Their movements began to gain ground in various principalities and kingdoms of northern Europe.

The great apostasy or disaffiliation from the Catholic Church prompted Pope Paul III to establish the Sacra Congregatio Romanae et Universalis Inquisitionis seu Sancti Officii (Sacred Congregation of the Roman and Universal Inquisition, or the Holy Office), in 1542. It consisted of a commission of six cardinals. They were at once the final court of appeal for trials concerning the Faith and the court of first instance for cases reserved to the Pope. It inaugurated an era of institutionalised inquisitions. Succeeding popes made further provisions for the procedure and competency of the Inquisition of which Pope Sixtus V is regarded as the reorganizer.
In that same year, the Pope made known the first list of books prohibited for their doctrinal content or criticism of the Catholic Church. A more comprehensive Index of Prohibited Authors and Books was brought out after the Council of Trent (1545-63). Later, a separate though related Congregation of the Index updated the list.
d) Paganism (16th century onwards)
This is an umbrella term for beliefs held by polytheistic religions. It applied especially to the religious beliefs of the natives of the colonies held by Portugal and Spain in Asia, Africa and Latin America. King João III of Portugal applied to the Pope for an independent Portuguese Inquisition to deal specifically with threats posed by crypto-Jews in his country. A branch of the tribunal was set up in the city of Goa in 1560 to handle cases relating to the ethnic Portuguese in India and to neo-converts to Catholicism (Jews, Hindus and Muslims) relapsing into their former religions or practising them side by side with Catholicism.
e) Heterodoxy (18th century onwards)
This refers to views that differ from right belief or purity of the Faith, or say, orthodox views. ‘Right belief’ is not subjective, as resting on personal knowledge and convictions, but that which is in accordance with the teaching and direction of an absolute extrinsic authority.
 Heterodoxy goes back to Protestant thought in Germany where attempts were made to support by reason the supernatural truths contained in the Holy Bible. In reality such experiments tended strongly in favour of Naturalism, which they had wished to condemn. Heterodox tendencies by so-called free thinkers or dissenters hacked at the sacred obligation of preserving the deposit of Revelation pure and undefiled. The most revolutionary in this regard were the French Encyclopaedists and others of their ilk in Europe and America.
Heterodoxy goes back to Protestant thought in Germany where attempts were made to support by reason the supernatural truths contained in the Holy Bible. In reality such experiments tended strongly in favour of Naturalism, which they had wished to condemn. Heterodox tendencies by so-called free thinkers or dissenters hacked at the sacred obligation of preserving the deposit of Revelation pure and undefiled. The most revolutionary in this regard were the French Encyclopaedists and others of their ilk in Europe and America.
Eventually, Rationalism, or the use of human reason or understanding as the sole source and final test of all truth, began to form the basis of intellectual and scientific activity. It seemed to hold out a promise of dramatic improvement in human life. These tendencies finally led towards religious disbelief, evident in such modes of thought as atheism, agnosticism, materialism, naturalism, pantheism, scepticism, and the like.
New Winds
In the first half of the nineteenth century, the stage was set for republican revolts against European monarchies, beginning in Sicily and spreading to France, Germany, Italy, and the Austrian Empire. They ended in failure, repression and widespread disillusionment among liberals.
Nonetheless, winds of liberalism kept blowing hard, unsettling the traditional ways of thinking. Reason continued to score points against faith and displace it across Europe. In fact, religious beliefs began to be equated with blind faith; so faith looked weird when juxtaposed with free private judgement. The view that orthodoxy should be maintained at all cost began to be looked upon with suspicion.
With religion itself relegated to the background, how could a mere institution that stood staunchly for preserving the deposit of the Faith be welcome? Here was a propitious moment for dissenters to quickly and impudently go about their business of discrediting the Catholic Church. The process that had started with the Protestant Revolution gained steam with the French Revolution. It is no wonder, then, that we moderns experience difficulty in grasping the rationale of the Inquisition. The punishments meted out by the tribunal for heresy seem exaggerated, not to say irrational and misplaced.
 The Inquisition tribunals worked intermittently in the eighteenth century until they were disbanded by the liberal or revolutionary governments of several European countries in the nineteenth century. The Roman Inquisition also came to a gradual end. In 1908, Pope Pius X renamed it Congregation of the Holy Office. A few years later its duties were merged with those of the Congregation of the Index. In 1965, Pope Paul VI reorganized the Holy Office, changing its name to the Sacred Congregation for the Doctrine of the Faith, and eliminated the Index in the following year.
The Inquisition tribunals worked intermittently in the eighteenth century until they were disbanded by the liberal or revolutionary governments of several European countries in the nineteenth century. The Roman Inquisition also came to a gradual end. In 1908, Pope Pius X renamed it Congregation of the Holy Office. A few years later its duties were merged with those of the Congregation of the Index. In 1965, Pope Paul VI reorganized the Holy Office, changing its name to the Sacred Congregation for the Doctrine of the Faith, and eliminated the Index in the following year.
How are we to explain the Inquisition in the light of its own period? To do justice to the topic, we need to first have a look at the broad features of the tribunal of the Inquisition.
(To be continued… Part 2)
The Two Abbés

Who in Goa hasn’t seen that striking bronze figure of a tall man in a flowing robe, with a lady tumbling down at his feet? Sculpted by Ramachondra Panduronga Kamat and erected next to the Adil Shah Palace, the statue is now in its seventy-fifth year. It was a tardy tribute to a nineteenth-century Goan celebrity – Abade Faria – considered the ‘father of modern hypnotism’.
For every passer-by that admires that lofty monument, there are thousands the world over who would be reminded of a literary character of the same name: Abbé Faria from Alexandre Dumas’ The Count of Monte-Cristo. This adventure novel was published a century before that statue was put up in Panjim.
Are the Abade and the Abbé one and the same person? Faria is a surname; abade and abbé mean ‘abbot’ in Portuguese and French, respectively. The historical Faria only served as a literary inspiration for the celebrated French writer. Some parallels are obvious between the two figures but not all of them do justice to the flesh and blood Faria.
The real Faria was born José Custódio de Faria, in Goa, then Portuguese India. After eight years of priestly studies and a doctorate in Rome, he lived in Lisbon for the same number of years. Finally, he settled down in Paris, where he spent over thirty years, with a year or so in Marseilles and Nimes. In France he was referred to as Abbé Faria.
Dumas’ learned Abbé is a linguist, philosopher, and a strong-willed man. Our Abbé was proficient in philosophy, theology, history, and he intuitively discovered hypnotism; he knew Konkani, Portuguese, Latin and French; and was a resolute man. The physical attributes of the two are similar, except for their height.

The novel is set in the bay of Marseilles, where the fictional Abbé is imprisoned; the real Abbé worked in that port town as a professor of philosophy, in 1811. The former is nicknamed ‘Mad Monk’ by the prison staff; quite intriguingly, our Abbé too was derided by doctors, writers and fellow pastors for his ideas on hypnotism, in Paris (1813-19). Similarly, the Abbé’s description of lodging and boarding in jail could well be a mirror image of the real Faria’s living conditions at the Orties convent. Dumas’ inspector of prisons would be the equivalent of an actor, Potier, who lampooned our Abbé in Jules Verne’s fateful play, Magnétismomanie.
Coming now to Abbé Faria’s tunnelling for three long years: it could be interpreted as the real Abbé’s quest for ideas and materials in support of his theory of sommeil lucide (lucid sleep). When they died of fulminating apoplexy, in their sixties, both characters had their books still unpublished. The real Faria’s book De la cause du sommeil lucide ou étude de la nature de l’homme (Of the Cause of Lucid Sleep or Study of the Nature of Man) came out posthumously; the remaining three volumes were untraceable, much like the jailed Abbé’s book that was never found.
While Dumas’ Abbé is an Italian, born in Rome; the Goan Abbé was born in the ‘Rome of the East’. The hero, Dantès, once journeyed to India, whereas José travelled from India to Europe, and never went back to his homeland. Interestingly, the fathers of both have important roles in their sons’ lives. Could Dumas have known that José’s father in Lisbon was under house arrest for his nativist ideas, and that many of the conspirators of 1787 in Goa met with a fate worse than death? Apparently, José’s father and Dumas himself were both republicans at heart.

Finally, the treasure that the Abbé highlights in the novel could be a pointer to the treasure that the historical Abbé Faria endowed us with, in the form of hypnotism: this has long been an invaluable aid to the physical and mental well being of humankind.
It is sad that Faria fans find it hard to separate fact from fiction: shrouded as he is in deep mystery, the real Faria comes out largely disfigured. But given that historians and medicos took no steps to fix that shortcoming, how can one fault Dumas for taking artistic licence? After all, the man who died, disdained and forgotten, on 20 September 1819, was kept alive in the pages of The Count of Monte-Cristo. It now behoves us to put the historical Faria on a pedestal much higher than the one on which he is placed in Panjim’s main square.
The Hypnotist in Holy Orders
 He is better known as a personage in Alexandre Dumas’ novel The Count of Monte-Cristo Chateaubriand mentions him, albeit in derogatory terms, in his memoirs. In Goa, he is only vaguely known for his father’s cry ‘Hi soglli bhaji!’ which instantly filled with confidence the faltering preacher son at the royal chapel at Queluz, Portugal.
He is better known as a personage in Alexandre Dumas’ novel The Count of Monte-Cristo Chateaubriand mentions him, albeit in derogatory terms, in his memoirs. In Goa, he is only vaguely known for his father’s cry ‘Hi soglli bhaji!’ which instantly filled with confidence the faltering preacher son at the royal chapel at Queluz, Portugal.
Precious little remains till date in the memory of the average Goan. There is a statue of him in the capital city and a street takes his name in Margão. He has been forgotten in his native village of Candolim; only a primary school is named after him there and in some other villages too. He is almost unknown where he worked and lived – Lisbon, Paris and Marseilles. Only an obscure street is named after him in Marseilles.
People may not be apt to remember somebody who lived two centuries ago and with a mysterious sounding name such as Abbé Faria. But what if he has some original scientific contribution to his credit? Never mind that he was a theorist of hypnotism by suggestion, which has since become a vital aid to psychiatry, psychoanalysis and surgery. Very often his name is omitted when the subject comes to the fore. Not even does the Encyclopaedia Britannica refer to him as they do Franz Anton Mesmer (1734-1815) and James Braid (1795-1860), who have only usurped his pride of place.
Such has been the fate of José Custódio de Faria (1756-1819), a priest and doctor of theology, who without any medical training did perceive and lend respectability to the true nature of what he called ‘sommeil lucide’ (lucid sleep). It was an intuition characteristic of a true genius. And for this original contribution to the field of science he is regarded at home as the greatest Goan that ever lived.
Early Life
José Custódio de Faria was born on 31 May 1756, to Caetano Vitorino de Faria of Colvale and Rosa Maria de Souza of Candolim. His father was a seminarian and had already received minor orders when he met and married Rosa, the only daughter of a rich landlord of Candolim. He was clever and she was rich, but the combination did not work out that well. Even their son born two years after their marriage, could not prolong their mutual love. Around the year 1764, they got a canonical decree of separation in 1764. He took holy orders and she joined the Santa Monica convent in the  old city of Goa.
old city of Goa.
No bonds linked them ever since. The father and the son stayed a few years at their friends in Candolim – the Pintos of the Conspiracy fame – and at Colvale too. On 21 February 1771, four years after being ordained a priest, Caetano Vitorino left for Lisbon, en route for Rome, to continue his priestly studies. He had similar intentions for his son. Their social circle in Goa and particularly a letter of recommendation they carried for the nuncio in Lisbon, Mgr. Inocencio Conti, won them access to the royal court. Moreover, the reigning monarch, Dom José I, and his prime minister, the Marquis of Pombal, were favourably disposed towards the Goans, whom they strongly recommended for civil, military and ecclesiastical positions at home.
Student in Rome
Thus José Custódio was awarded a scholarship to study in Rome. The father returned to Lisbon in 1777 on attaining a doctorate to further his objective of objective of being appointed the bishop of Goa. His great disappointment and frustration on this count determined much of what followed in his life and his son’s too.
José Custódio stayed on and was ordained on 12 March 1780. At 24 he completed his doctoral thesis titled Theologicae Propositiones: De Existentia Dei, Deo Uno et Divina Revelatione (Theological Propositions on the Existence of God, One God and Divine Revelation) and joined his father in Lisbon.
The duo were good friends but a different purpose animated them. Caetano Vitorino, the more political minded and diplomatic of the two, was fully immersed in matters Goan. He was a sort of self-appointed protector of and influential reference for the Goan community. The Court had been impressed by the fact that, though immensely influential at the highest levels of the kingdom’s administration, he had never asked favours for himself, though it was known that his personal finances were far from bright. But then, intelligence reports began to pin him down as the mastermind and coordinator in Lisbon of a political revolt at home in 1787. As soon as news of this reached Lisbon, they hunted for the duo and their good friends, clerics and laymen.
Meanwhile, all except Fr. Caetano Vitorino had fled to Paris, reportedly to meet and discuss with their envoys of Tipu Sultan, who proposed to be on the French side in their ascendancy against the British in India, but nothing was confirmed in this respect. Others believe that simpler reasons motivated Fr. José Custódio’s sudden departure – that he was attracted by the intellectual climate of France. His father did, however, stay back, still persevering in his designs and probably even overestimating his influence with the high officialdom. He was then put under house arrest in the Carmelite convent where he gave his priestly assistance, and probably died in 1799.
In Paris
Nothing is known of Fr. José Custódio’s activities in the French capital except that he was accused, in 1792, of being a gambler and frequenter of the Palais-Royale. He was acquitted, or at least no action was taken against him by the police. Three years later, on 5 October 1795, he led a battalion of revolutionaries against the National Convention. This political stand made him popular with the supporters of the Directoire and won him the friendship of the Marquis de Chastenet de Puységur.
The latter relationship was decisive. The Marquis had been a disciple of Mesmer whose quackish furrows into ‘animal magnetism’ and tall claims of cures had initially won him the acclaim of high Parisian society. But, in 1785, his exit was shameful. The Marquis, on the other hand, was an honest, well-meaning and cultured person, who took over from where Mesmer had left. Dr Egas Moniz, the Portuguese Nobel Prize Winner and biographer of Fr. José Custódio de Faria, speculates that he acquired knowledge of magnetism in Paris after he struck up an acquaintance with the Marquis.
The first news of Fr. Faria’s activity as a magnetizer is of the year 1802, in the memoirs of Chateaubriand (published in 1843), who referred to his experiments in derogatory terms. He had dined with Fr. Faria at the house of the Marchionesse of Custine. Here, Fr. Faria reportedly declared that he could kill a canary by magnetizing it. However, when the magnetizer was put to the test, he failed, which led Chateaubriand to conclude: ‘O Christian, my presence itself will be enough to make the tripod ineffective!’ Chateaubriand was a devout Catholic. He had strong reservations against magnetism – because of the Church’s attitude of suspicion towards it. But what is more is that Fr. José Custódio de Faria was a Catholic, no less!
Fr. José Custódio continued his research into the subject up to the year 1811, when he was appointed professor of Philosophy at the Academy of Marseilles. The Imperial Almanac of 1811 records that he lived there a year and was elected member of a medical society. Since he had no medical qualifications, the membership can only be attributed to his skills as a magnetizer. But for some mysterious reason, he was transferred, in fact, demoted, to the post of auxiliary professor at the Academy of Nimes. He felt slighted and frustrated and, unaccustomed as he was to life in a small city like Nimes, he returned to Paris, in 1813, in search of greener pastures. Unattached to any institution, he initiated his course in magnetism on 11 August 1813, 49, Rue de Clichy.
Sessions

The sessions were held every Thursday, on an admission fee of five francs only. He began with a lecture in halting French. The audience, which consisted largely of women, paid scant attention to this part of the session; their eyes were set on what was to follow – his experiments to substantiate his theory.
Contrary to the claims made by Mesmer, the he could control the body fluids of his patients and rectify their course through special methods invented by him, Fr. José Custódio very humbly put forth that not all individuals could be hypnotised, and that the degree of response to his hypnotic powers necessarily varied from person to person. He was the first to establish that hypnotism was a science of suggestion.
Fr. Faria’s method consisted of a series of well-reasoned and effective actions: he got the patient to sit comfortably and, through concentration, to relax, imagining that they were going to sleep. When the patient was ‘tranquil’, he gave the command, ‘Sleep!’ and, if necessary, repeated it, with a certain degree of urgency, three or four times. If he failed, he would either sportingly give up or try other methods.
The sessions became the rage of the town. There were detractors, critics and skeptics, no doubt. Once, a journalist attended his session and then unjustly criticised and ridiculed the priest in the press. At another session, a leading stage actor, Potier, offered himself for his experiments. He feigned to be in a trance and suddenly rose to say, ‘Ah, Abbé! If you magnetize others as well as you magnetized me, you don’t seem to be doing much.’
Fr. José Custódio put up very well with all such betrayals. He also withstood quite stoically criticism from the clergy and Rome, who then viewed his experiments with suspicion always on the look-out for diabolical influences therein. But the priest always expressed respect for the Church and a firm desire to stay within the Catholic fold. ‘Un esprit supérieur,’ as his disciple Gen. Noizet said of him, he wished to convince the Church that his experiments were fully within the natural realm and that there was no magic or witchcraft involved.
Thus, Fr. Faria took everything in its stride. Only once did he break down, when at Potier’s request the playwright Jules Verne put up a play, on 5 September 1816, the Variétés, titled La Magnétismomanie, ridiculing the Goan priest.
Sad end
The time was now ripe for Fr. Faria to stop his activities. He retired soon thereafter, rendering priestly services in exchange for boarding and lodging.
During the last years of his life, he decided to organize his material in book form. It was an ambitious project in four volumes, of which only the first one is known to have appeared. It is his magnum opus is titled De la cause du sommeil lucide ou Étude de la nature de l’homme (On the Cause of Lucid Sleep or Study on the Nature of Man). In it he referred to the shameful play:
‘With regard to Magnétismomanie, I cannot ask which laws permit the modern Terence to expose an unknown foreigner to public ridicule. I presume that even the savage would be ashamed to insult his kind, which has nothing in common with actors and the theatre.
‘Far from me the idea to disturb public pleasures: But I might have added to Magnétismomanie a new scene – an extremely pungent one – had my condition not prevented me from doing so, and had my own aversion for such amusements not kept me away from playhouses.’
According to one biographer, by a strange coincidence, the day of his death, also marks the release of his book. His famous words, ‘There are evils that sometimes do good to those who discern their utility,’ might have very well served as his epitaph – if only he had the money for a decent burial. He died at the age of 63, unsung as he was born. A life full of ironies, for born of a rich family he died poor; born of parents who were in love, they separated after his birth; a man with original contributions to posterity, he died with no godfathers to promote his name.
(Herald Illustrated Review, Panjim, Goa. Vol. 95, No. 30, February 1-15 1995. Slightly updated version)


